Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome (FAIS) Treatment Options
What is Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome (FAIS)?
Femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS) is a condition characterized by abnormal contact between the proximal femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum (hip socket) during hip movement. This contact can lead to pain, limited range of motion, and functional impairment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for FAIS is essential for effective management and improved quality of life for affected individuals.
How is FAIS treated?
Treatment for FAIS aims to address the underlying cause, alleviate symptoms, and restore function by allowing impingement-free motion in the hip joint. The treatment approach varies depending on the symptom’s severity, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health, and the specific anatomical abnormalities contributing to the condition. Treatment options may range from conservative measures such as physical therapy and activity modification to surgical intervention in more severe cases.
What non-operative options are available?
Physical Therapy
Targeted exercises to strengthen hip muscles, improve joint stability, and enhance flexibility.
- Strengthening Exercises: Tailored exercises focus on strengthening the muscles surrounding the hip joint, including the abductors, adductors, flexors, and extensors. By improving muscle strength and control, these exercises help stabilize the hip joint and reduce impingement-related symptoms.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle stretching and mobilization exercises are incorporated to improve hip joint flexibility and alleviate stiffness. Enhanced range of motion promotes smoother joint movement and reduces discomfort during daily activities.
- Core Stability Training: Core strengthening exercises target the muscles of the abdomen, pelvis, and lower back, which play a crucial role in supporting hip stability and proper biomechanics. A strong core helps distribute forces more efficiently, reducing strain on the hip joint and minimizing impingement.
- Functional Movement Training: Functional exercises simulate real-life movements and activities to improve coordination, balance, and proprioception. By enhancing dynamic stability and movement control, functional training reduces the risk of injury and improves overall functional capacity.
- Education and Self-Management Strategies: Patients receive education on proper body mechanics, activity modification, and self-management strategies to optimize their recovery and prevent recurrence of symptoms. Empowering individuals with knowledge and skills to manage their condition effectively is essential for long-term success.
Activity Modification
Modification of activities that exacerbate hip instability is essential to prevent further damage and promote healing. Patients may be advised to avoid high-impact activities such as running or jumping and to engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling. Additionally, proper warm-up and stretching exercises before physical activity can help reduce the risk of injury.
Orthotic Devices
Custom orthotic devices or bracing may be prescribed to provide additional support and stability to the hip joint. Orthotics can help correct biomechanical abnormalities, redistribute forces across the joint, and alleviate symptoms associated with hip instability.
Pain Management
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with hip instability. These medications can provide temporary relief while other conservative measures are implemented.
What operative options are available?
Arthroscopic Hip Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure performed using small incisions and specialized instruments. It allows Dr. Shane J. Nho to visualize the inside of the hip joint and address various abnormalities, including:
- Labral Repair: Repair of labral tears or debridement of damaged tissue to restore normal hip joint mechanics and stability.
- Labral Reconstruction and Augmentation: In cases when the labrum is deficient or is unable to be repaired, Dr. Shane J. Nho can reconstruct or enhance the labrum through use of one’s own tissue or donor tissue.
- Capsular Plication: Tightening of the hip joint capsule to reduce excessive joint laxity and improve stability.
- Impingement Correction: Removal of bony impingement or reshaping of the hip joint structures to alleviate impingement and prevent further damage.
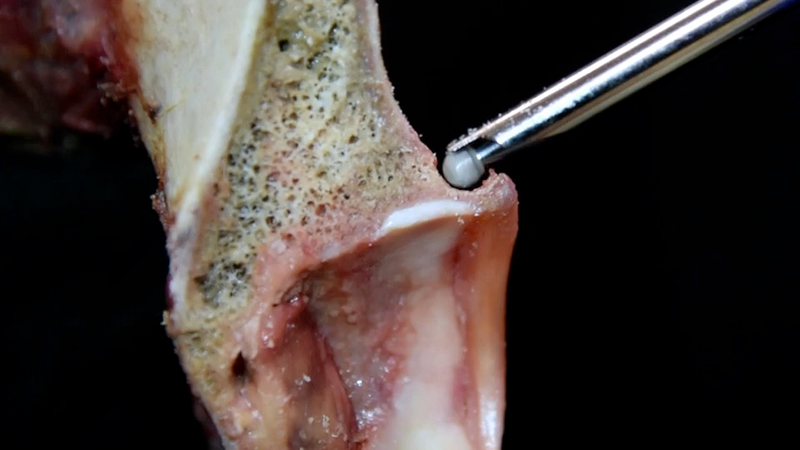
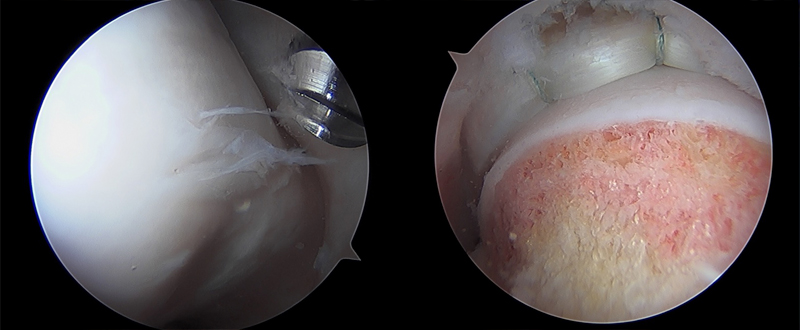
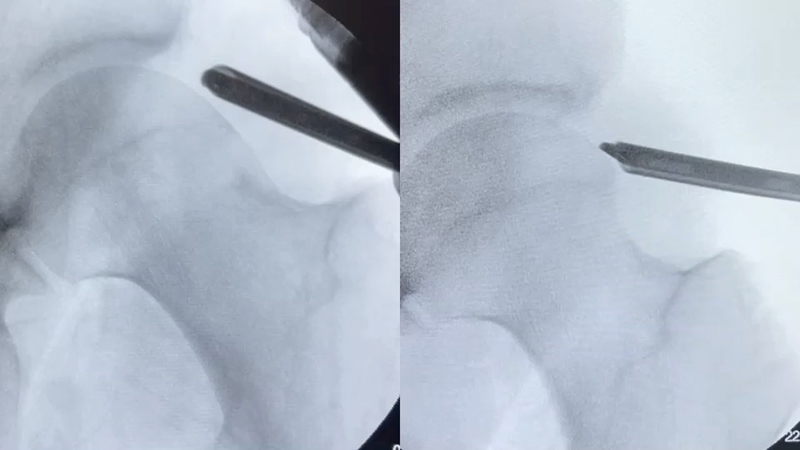
Open Surgical Procedures
In some cases, open surgical procedures may be necessary, particularly for complex or severe cases of hip instability. These procedures may involve:
- Periacetabular Osteotomy: Surgical realignment of the pelvis to improve hip joint stability and reduce the risk of dislocation, particularly in cases of hip dysplasia.
- Hip Replacement: In severe cases of FAIS associated with advanced osteoarthritis or irreparable joint damage, total hip replacement surgery may be considered to restore function and alleviate pain.
What does rehabilitation look like?
Rehabilitation following surgical intervention is crucial for optimizing outcomes and restoring function to the hip joint. Physical therapy is typically initiated shortly after surgery to promote healing, improve joint mobility, and gradually reintroduce weight-bearing activities. The rehabilitation process may involve a progressive exercise program, manual therapy techniques, and patient education on proper body mechanics and activity modification to prevent recurrence of FAIS.
In conclusion, the treatment of FAIS requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying cause, alleviates symptoms, and restores stability and function to the hip joint. Conservative measures such as physical therapy, activity modification, and orthotic devices may be effective for mild to moderate cases, while surgical intervention may be necessary for more severe or complex conditions.
Dr. Shane J. Nho is a board-certified fellowship trained sports medicine orthopaedic surgeon who specializes in the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome. If you believe you are affected by femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, schedule a consultation today with our experienced orthopaedic care team.
At a Glance
Dr. Shane Nho
- Board-certified, fellowship-trained orthopedic surgeon
- Team Physician for Chicago Bulls, White Sox, Steel
- Performs more than 700 procedures each year
- Learn more
